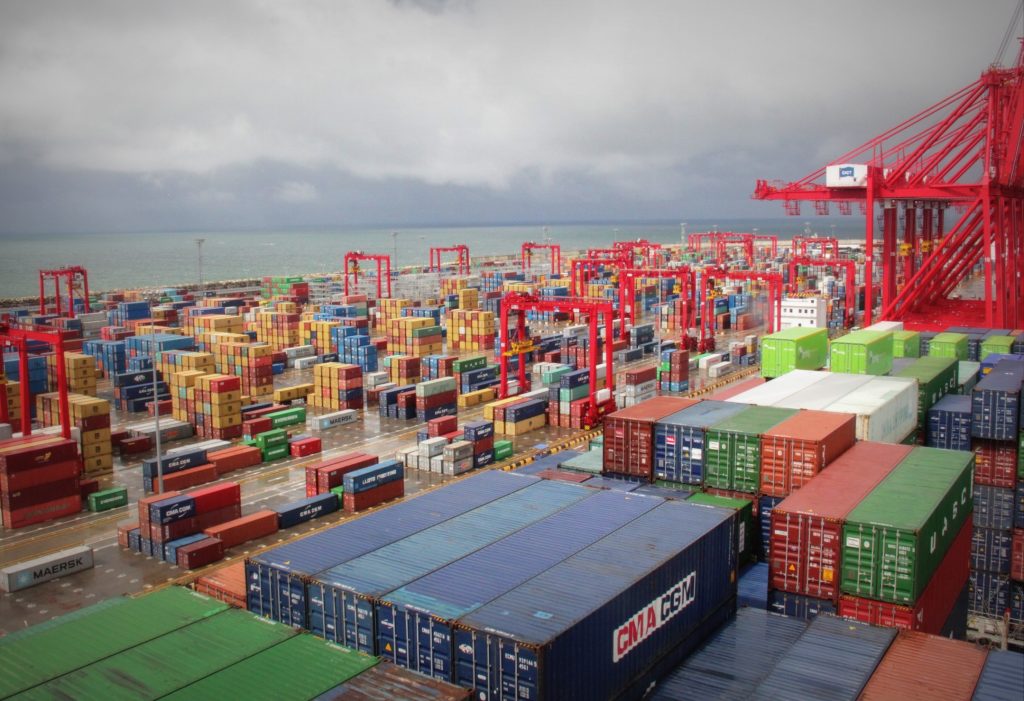
India’s containerised trade with the world has enjoyed a spirited uptick in the first quarter of calendar 2018, as it beat the country’s past performance in export-import growth over eight quarters. Imports witnessed a material increase of 16 per cent, with exports also growing at a healthy pace of 7 per cent. Together, they led India’s trade to a strong start this 2018, as per a Maersk India Trade Report for the quarter.
“These numbers become more relevant when viewed through a global lens. They are significantly higher than estimated global containerised demand growth of 3-4 per cent,” explains Mr Steve Felder, Maersk Line Managing Director for India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and Maldives.
Imports
The key contributor to import growth during this period was dry cargo (commodities that aren’t liquid or perishable), which jumped by 22 per cent. This contrasts with the corresponding period last year when the segment grew only 2 per cent. Recyclables, namely, paper and metal, were the two dry cargo commodities that led this growth and registered strong 61 per cent and 55 per cent increases, respectively. A large portion of these commodities came to India from North America and Europe, and helped North and West India imports rise by 3 per cent and 13 per cent, respectively.
“Recyclable commodity imports were severely impacted by demonetisation. With the rebound we’ve seen in this category now, it would be safe to assume that the effects are finally wearing off and domestic consumption is on the rise,” says Mr Felder.
“Additionally, China’s recent decision to increase restrictions on waste paper imports benefited India, which is a major importer of this commodity for local recycled paper manufacturing. Together, these key developments have augured well for India’s import growth.”
Exports
On the export side, rocketing demand for Indian made vehicles in Turkey, and Indian fruit and nuts in the UK and the UAE, pushed growth to a healthy 7 per cent.
“The first quarter has been a fairly constructive period for export growth as well. As the effect of policy shifts faded and the inflow of GST refunds began, it created surplus capital in the hands of local manufacturers. The market was further buoyed by a weaker rupee, which, in turn, increased India’s exports to the world,” adds Mr Felder.
East India witnesses highest export decline
A comparison of the export performance of India’s four regions shows that East India saw the highest decline in exports this year at -6 per cent growth. This was the result of a significant fall in the metal segment (mainly aluminium, ferro and steel) and rice exports originating from the region. These are estimated to have dropped by 12 per cent and 20 per cent, respectively. In contrast with Q1 last year, East India led the country’s overall export growth at 29 per cent.
“Rice exports overall have been weak this year, while the metals segment, mainly ferro and pipes, wasn’t competitive in global markets, which led to this stark decline,” explains Mr Felder.
The region’s metal exports fell across all its key destination markets, while the highest drop in rice exports was witnessed in the Mediterranean and West Africa markets.
On the other hand, imports of pulses into East India saw an upward climb, particularly chick peas and yellow peas from Canada and Turkey.
Indian made vehicle exports lead India’s overall export growth
At 18 per cent export growth, Indian made vehicles gained in demand across Africa, Latin America and Turkey. This was largely led by the 2-wheeler and 3-wheeler segments.
“With India fast becoming a key automotive manufacturing hub, OEMs across the board are investing in increasing their production capacity in the country. This is, in turn, also benefiting the auto ancillaries’ industry, and creating a multiplier effect in auto exports from India,” says Mr Felder.
Vehicle exports were largely driven by Western India, which clocked an impressive 71 per cent growth, up from 13 per cent last year.
On the import side, vehicles from Germany registered a strong uptick with imports coming into South India which is one of the major auto assembly hubs for the industry.
Overall automobile imports to this region saw a significant turnaround going from a contraction of 12 per cent last year to a robust 28 per cent growth in the corresponding period this year.
Reefer trade growth slows down
India’s overall reefer (refrigerated cargo) trade growth slowed on the export as well as import side. However, a strong increase was registered by exports of commodities like pharmaceuticals to North America and grapes to North Europe.
On the import side, inflow of reefers slowed. This was due to a slowing growth from Mediterranean countries (8 per cent up, from 82 per cent up last year) and contraction of 33 per cent from North Europe (compared to a 35 per cent increase last year).
“Countries across the world are considering policies to reduce their healthcare spending, and pharmaceuticals contribute a major portion of these expenses. The cost arbitrage India offers, combined with improving quality in manufacturing, is contributing to India’s growing play in pharmaceutical exports. Exports of grapes, on the other hand, are more cyclical and seasonal in nature,” explains Mr Felder.
Growth trend to continue through upcoming quarters
With large trading economies such as China and US sparring over their trade relations, India as well as other emerging countries are expected to witness strong inflows of select commodities.
Says Mr Felder, “Commodities have to find markets, and as India’s domestic consumption continues to rise, we can expect to see many of them find takers here. Also, the increasing aspiration of India’s populace will sustain this trend over the months to come, assuming there are no significant policy changes.”